ABOUT
S3D is a 3D printing label, which stands for passion, reliability and precision. The focus lies on high resolution 3D prints achieved with the newest stereolithography (SLA) technology. Having gained experience studying architecture at the Technical University of Innsbruck and at the University of Applied Arts in Vienna, S3D is concentrating mainly on 3D prints for architecture models without blench working on new frontiers.
[G]8
A framework for a selfhealing shelter
BACHELORTHESIS
2014
studio theodore spyropoulos
university of innsbruck
with christopher mellin, jasmin nast & stephan reifer
The bachelorthesis at the univerity of innsbruck is a one year work, divided into two parts. A research part and a design/project part. The complete work shows a system, a process and a design. The system in the project is a building system. It includes an adaptive formwork to build various edifices and a self-healing material for shapes.The process is shown from the form and material studies, over material and system tests, to the design. The design shows the complete research part combined in a designed project wich includes the system and the process. Finally, the design is the result of all these aspects and the paradigms to demonstrate that all the aspects are compatible and act togheter. The idea is a concept for a fast, simple and uncomplicated construction of pneumatic living forms. The project includes preassembled shells which can be blown up and covered up with the self-healing material. Mainly the units - or rather the clusters - are anticipated to be inhabited for a temporarily delimited amount of time.
CONCEPT
Concerning the construction studies, some pneu experiments with different shapes were conducted. The form and the cavity of the ribs is steadily rising. To some extent, the cavity of the ribs cannot only be used as part of the static aspect, but also as a room divider.
Thereafter, some experiments were made concerning the interaction of different forms. On the one hand, analogue model studies made a familiarization with the material possible. It showed how the material would be affected by external influences which were created by using spring steel wire lines, wooden balls and a spring steel wire grid, while the material was inflated with air. With regard to the findings, the static aspect is therefore based on panicles/ribs and patterns and inspired by antique ecclesiastical architecture and beamed ceilings. On the other hand, digital model studies were conducted. They combined the above mentioned findings and enabled the creation of a huge variety of models and studies of different forms and the documentation of the production steps. Through this static system interesting surfaces and even more interesting inner volumes are created.

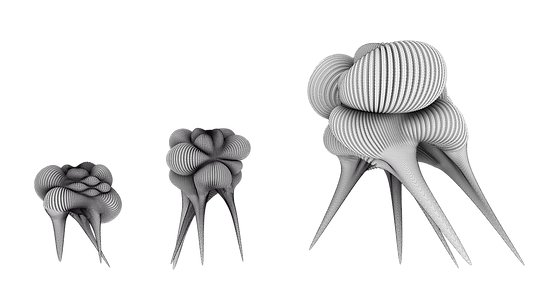
the arrangement of more units yields to a cluster. every cluster can look differently, depending on the type of units. Also the number and scale of the units within the cluster can vary.
Concerning the construction studies, some pneu experiments with different shapes were conducted. The form and the cavity of the ribs is steadily rising. To some extent, the cavity of the ribs cannot only be used as part of the static aspect, but also as a room divider.
Thereafter, some experiments were made concerning the interaction of different forms. On the one hand, analogue model studies made a familiarization with the material possible. It showed how the material would be affected by external influences which were created by using spring steel wire lines, wooden balls and a spring steel wire grid, while the material was inflated with air. With regard to the findings, the static aspect is therefore based on panicles/ribs and patterns and inspired by antique ecclesiastical architecture and beamed ceilings. On the other hand, digital model studies were conducted. They combined the above mentioned findings and enabled the creation of a huge variety of models and studies of different forms and the documentation of the production steps. Through this static system interesting surfaces and even more interesting inner volumes are created.
SHELL
The surface of the unit is fragmented into many little single parts through a processing software in order to connect them to a pneu. The material for the shell is going to be PVC membrane because of its adequate characteristics. It is primarily an extremely resistant and dense material. Moreover, it is resistant against cold, rotting and werldseam. PVC is useable more often which makes it a very ecological process. After the processing, the single parts are cut out of the PVC material with a CNC cutting machine and are numbered. Then, the parts are welded and hermetically sealed by a laser in order to be blown up as adaptive formwork. The air pressure has to be unchanging. The laser method used is called „overlapping procedure“. During this process, the laser stream interfuses the above lying join partner and is absorbed by the underlying one. Its heating leads to the plastification which bridges the gap of the raw material and heats the above lying join partner by heat conduction. Both layers are hardening by the pressure from outside and become a high quality welded connection.

deflated / inflated / sprinkled shell
ENVIRONMENT & MATERIALLITY
Pykrete is a biological and self-regenerating material. therefore a self-healing casing is possible. . it was used for the first time in World War II by Geoffry Pyke. he was ordered to build an aircraft carrier for the British Royal Navy, called Habbakuk. it weighed 2.200.000 t and took three summers to melt in a lake in Canada. pykrete has a remarkably low rate to melt because of its low thermal conductivity. It is obviously better than usual ice. Because of the material, building lots is limited to rather cold climatic zones. Still, it would be realizable everywhere with the right low climate.

suitable zones

Fused materials are never going to be separated again. A correctly executed weldseam has a 100% endurance limit. Before the weldseam is going to break at the weldseam point, it breaks somewhere else.(cf. Werner G. Sohn SOHN Kunststoff-verpackungswerk.)
THE cOATING
The final step combines all of the above experiments and findings and leads to their implamentation. The design includes three basic forms with legs. Those legs create a roofed protected space under the actual living place. Moreover, the entrance cannot be snowed in. Also the development of the living capsule is partly based on the legs because the ribs are arranged stair-like.
There are three different formworks, each form is one unit. The first is the small unit which is 6m high and provides space for 1 - 3 people. The middle formwork is 9m high and offers room for 2 - 6 people; and the big formwork is 15m high and big enough for 5 - 9 people. The construction elements can be docked together deliberately, but when one unit is finished, the other one has to adapt to it. The number of units has no limits. The arrangement of more units is a cluster. every cluster can look differently, depending on the type of units. Because of the three different types of units the customers can choose the number of pneus they want to have for their cluster and also the adjustment of the latter, so no cluster will ever look like another one. The interior room is a haptic allurement. Tt is very soft, fluffy, cozy and invites to put off one‘s clothes and cuddle up to the walls. You are cut off from the cold outside, you can relax and lay back in silence. In the white ambience of the casing you feel like newly born and you can refill your power for the next day.



